Emails are one of the most common forms of communication in both personal and professional life. Every day, billions of emails are sent around the world. But do you ever wonder how these emails travel safely from one computer to another without getting lost or stolen? The answer lies in email protocols like SMTP and encryption methods like TLS.

In this blog, we will explain everything you need to know about SMTP and TLS encryption effortlessly.
Table of Contents
Pricing
| Trail Plan | Standard Plan | Premium Plan | Professional Plan |
| $50 | $145 | $185 | $225 |
| Sending Limit | Sending Limit | Sending Limit | Sending Limit |
| 1000 Emails/Hour | 1500 Emails/Hour | 3000 Emails/Hour | 5000 Emails/Hour |
What is SMTP?
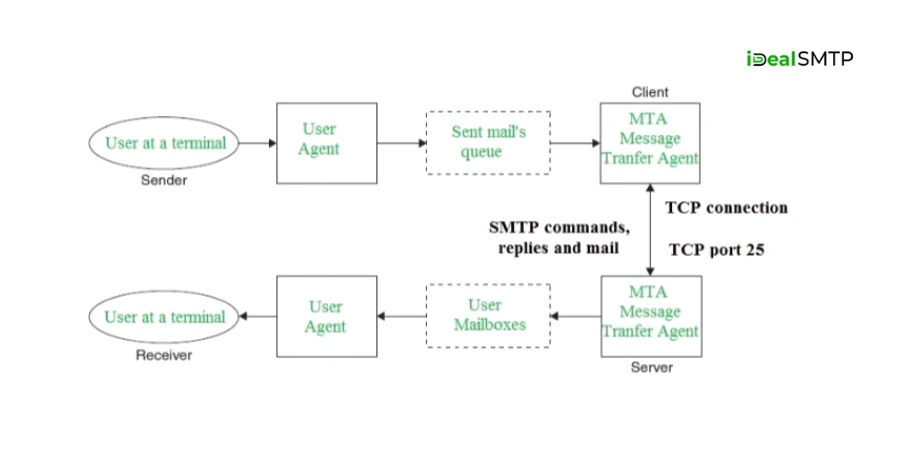
SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. It is the standard method used to send emails across the Internet.
When you send an email from your email client (like Gmail, Outlook, or Thunderbird), SMTP is the system that takes your message and delivers it to the recipient’s mail server. Think of SMTP as the postman of the internet– it picks up your message, figures out where to send it, and makes sure it reaches the right destination.
Why SMTP is Important
When you send an email, it doesn’t go directly to the receiver. It first goes through an SMTP server. This server checks and forwards your email to the receiver’s mail server. Without SMTP, your emails would have no direction and might never reach their destination.
How SMTP Works
SMTP works like a digital postman. Here is a simple flow of how it works:
- You compose and send an email.
- Your email client (like Gmail or Outlook) sends the email to the SMTP server.
- The SMTP server checks the destination and forwards the email to the right mail server.
- The recipient’s email server receives the email and stores it.
- The receiver can then open and read the email.
This whole process happens in just a few seconds.
What is TLS?
TLS stands for Transport Layer Security. It is a security protocol that helps protect data when it’s sent over the internet. In simple words, TLS encrypts your information so that no one else can read it while it’s being transferred.
Think of TLS like a sealed envelope for your digital data. When you send an email, TLS wraps your message in a secure layer so that hackers or unwanted people can’t see what’s inside while it travels to the recipient.
Purpose of TLS
TLS makes sure that the data (like your email) is not visible to hackers or third parties while it travels through the internet. Without TLS, your email content, including sensitive information like passwords or credit card numbers, can be read by anyone.
Why TLS is Important
Without TLS, emails and other online data are sent in plain text, which means anyone on the network (like public Wi-Fi) could read or steal your information. TLS solves this by:
- Encrypting the data during transmission
- Protecting sensitive information like passwords, personal messages, and attachments
- Preventing tampering or message modification
TLS is widely used not just in email, but also in secure websites (that’s why you see https:// instead of http:// in the browser).
Why Encryption is Needed in Emails
Emails travel through many networks before reaching the receiver. During this journey, your data can be seen or stolen by hackers if not protected. Here’s why encryption matters:
- Privacy: Keeps your message safe from others.
- Security: Prevents hackers from stealing information.
- Trust: Builds confidence between the sender and the receiver.
How SMTP and TLS Work Together
SMTP and TLS work together to send your emails safely and securely across the internet.
- You compose and send an email
You use an email service like Gmail, Outlook, or any email client. You hit “Send.” - SMTP takes over
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) starts the job of delivering your email. It connects to the recipient’s mail server and begins sending your message. - TLS adds a security layer
Before sending the actual content, your email server says, “Hey, can we encrypt this?” This process is called STARTTLS — it’s a command that upgrades the connection from regular to encrypted. - If both servers support TLS
If your server and the recipient’s server both support TLS, a secure channel is created. This means your email travels encrypted, so no one can read or change it during transmission. - The email is delivered
Once securely transmitted, the email is received by the recipient’s mail server, and they can open it normally.
The default SMTP is Not Encrypted
By default, SMTP does not encrypt emails. This means emails sent through plain SMTP can be read by anyone who intercepts them. This is where TLS comes in.
SMTP with TLS
When SMTP is used with TLS (also known as STARTTLS), it adds a layer of email encryption between the sender’s and receiver’s servers. This means the email is converted into unreadable data that can only be understood by the receiver’s server.
What is STARTTLS?
STARTTLS is a command that upgrades a plain-text connection to a secure one using TLS. When your email server supports STARTTLS, it will try to encrypt the connection before sending the email.
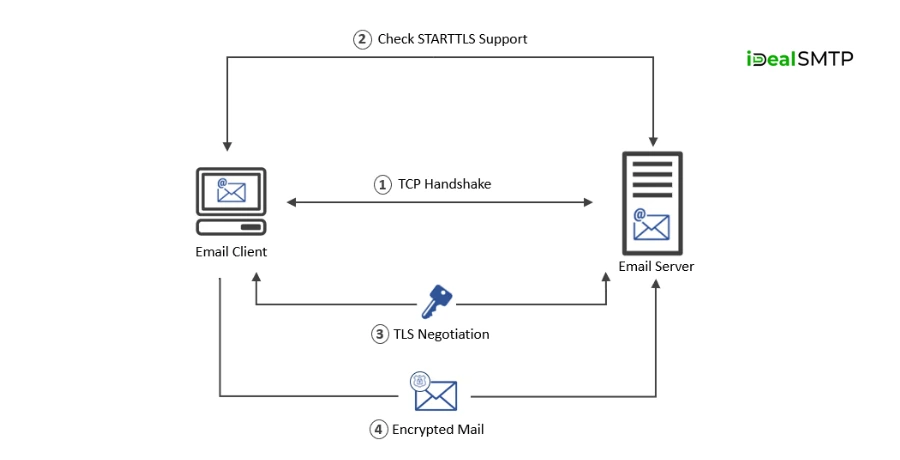
Benefits of STARTTLS
- Provides email encryption without changing the SMTP port number.
- Works with existing email infrastructure.
- Widely supported by email providers.
TLS vs SSL
Many people confuse TLS with SSL. Here is a clear explanation:
What is SSL?
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. It was the earlier version of TLS. While SSL is now outdated, many still use the term when they mean TLS.
Difference Between TLS and SSL
- TLS is more secure than SSL.
- SSL is no longer used in modern email systems.
- TLS is faster and uses stronger encryption algorithms.
SMTP Ports and TLS Encryption
There are several ports used by SMTP. Some are encrypted, and some are not.
Port 25
- Used for sending emails between servers.
- Usually not encrypted.
- Often blocked by ISPs to prevent spam.
Port 465
- Used for SMTPS (SMTP over SSL/TLS).
- Encrypted by default.
Port 587
- Recommended for email submission.
- Works with STARTTLS.
- Secure and commonly used.
Types of TLS Encryption
TLS encryption can be of different types based on how it’s applied:
Opportunistic TLS
- Email is sent encrypted if the receiving server supports TLS.
- If not, email is sent in plain text.
Enforced TLS
- Email is only sent if the receiving server supports TLS.
- If TLS is not available, the email is not sent.
How to Know if Your Email is Encrypted
Most email services show a small lock icon to indicate if your email is encrypted. If you use Gmail, you might have seen a red or green padlock. This tells you whether the email was sent securely or not.
Risks of Not Using TLS
If you do not use TLS with SMTP, your email data is at risk. Here are some dangers:
- Hackers can read your emails.
- Sensitive information like passwords can be stolen.
- Emails can be modified during transmission.
- Your email reputation can suffer.
TLS Certificates
TLS uses digital certificates to prove the identity of the server. These certificates are like ID cards. When you connect to a server, the certificate proves that you are really talking to the right server.
How Certificates Work
- Your email client connects to a server.
- The server shows its TLS certificate.
- Your client checks if it is valid.
- If valid, the secure email connection starts.
Email Providers That Use SMTP with TLS
Many popular email providers use TLS with SMTP:
- Gmail
- Outlook
- Yahoo Mail
- Zoho Mail
- ProtonMail
These services encrypt your emails during transmission, making them much safer.
SMTP Authentication and TLS
SMTP authentication is the process by which the sender proves they have permission to send emails. This is usually done with a username and password. When used with TLS, the credentials are also encrypted, making the process even more secure.
Common Problems and How to Fix Them
Even though SMTP and TLS make sending smooth and secure emails, sometimes you may run into problems. Here are the most common issues and how to fix them.
1. TLS Not Supported by the Server
Problem:
The sending or receiving mail server does not support TLS. This means your email might be sent without encryption.
Fix:
- Use a reliable email provider that supports TLS (like Gmail, Outlook, or Zoho).
- If you manage your server, make sure TLS is enabled and updated.
- Ask your recipient to check if their server supports TLS.
2. Incorrect SMTP Port Configuration
Problem:
You’re using the wrong port number to send emails. Common SMTP ports are:
- Port 25: Not secure, often blocked by ISPs
- Port 465: Secure SMTP over SSL
- Port 587: Secure SMTP with STARTTLS (recommended)
Fix:
- Use port 587 for best results with TLS.
- Check your email client or server settings and update the port.
3. STARTTLS Command Fails
Problem:
The STARTTLS command is rejected or fails during the handshake. This stops the secure connection from being established.
Fix:
- Ensure both the sender and receiver support STARTTLS.
- Check your email server’s logs for specific error codes.
- Update your mail server software and TLS certificates.
4. Expired or Invalid TLS Certificates
Problem:
If your server’s TLS certificate is expired or not trusted, email clients may refuse to connect securely.
Fix:
- Renew expired certificates regularly.
- Get your TLS certificates from a trusted authority like Let’s Encrypt or DigiCert.
- Make sure the certificate is installed properly.
5. Firewall or ISP Blocking SMTP Ports
Problem:
Some ISPs or firewall settings block common SMTP ports, especially port 25.
Fix:
- Use port 587 with TLS for better compatibility.
- Adjust your firewall to allow email traffic through the correct port.
- Contact your ISP if you’re unsure which ports are allowed.
6. Authentication Errors
Problem:
SMTP servers often require authentication (username and password). If your credentials are wrong or missing, sending will fail.
Fix:
- Double-check your email and password.
- Make sure “SMTP authentication” is enabled in your email client.
- If using app-specific passwords (like in Gmail), make sure it’s updated.
7. Email Goes to Spam Folder
Problem:
Even when using TLS and SMTP properly, emails may end up in spam folders.
Fix:
- Check your domain’s SPF, DKIM, and DMARC settings.
- Avoid spammy words and attachments.
- Keep your email content clean and relevant.
TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3
These are the latest versions of TLS:
TLS 1.2
- Very secure.
- Widely supported.
- Used by most email providers.
TLS 1.3
- Even more secure.
- Faster performance.
- Being adopted gradually.
Best Practices for SMTP and TLS
- Always use port 587 with STARTTLS.
- Use strong passwords for SMTP authentication.
- Regularly update your TLS certificates.
- Monitor email delivery and errors.
- Use reliable email providers.
The Future of Email Security
Email security is constantly improving. New standards like MTA-STS (Mail Transfer Agent Strict Transport Security) and DANE (DNS-based Authentication of Named Entities) are being used to make email transmission even more secure.
These protocols force email servers to use encryption and check TLS certificates before delivering emails. This ensures better privacy and protection against spoofing and hacking.
Conclusion
SMTP is the backbone of sending emails, and TLS is the shield that protects them. Together, they make sure your emails are delivered safely and securely. In a world where data privacy is more important than ever, using TLS with SMTP is not just a choice, it’s a necessity.
By understanding how these technologies work, you can ensure your emails stay private, safe, and trusted. Whether you’re a business owner, marketer, or just someone who sends emails regularly, knowing about SMTP and TLS encryption can help you stay secure online.
FAQs
Here are the top FAQs on SMTP and TLS Encryption
Is TLS better than SSL?
Yes, TLS is newer and more secure than SSL.
What port should I use for secure SMTP?
Port 587 with STARTTLS is recommended.
Does SMTP alone make emails secure?
No, SMTP by itself does not encrypt emails. Your messages can be read if intercepted. That’s why encryption methods like TLS are needed.
What is TLS in email communication?
TLS stands for Transport Layer Security. It encrypts your email data while it’s being sent, so hackers or anyone spying on the connection can’t read it.
How do SMTP and TLS work together?
SMTP handles the delivery, and TLS ensures the delivery is secure by encrypting the email before it travels over the internet.
What is STARTTLS?
STARTTLS is a command that upgrades a normal SMTP connection to a secure one using TLS encryption. It ensures your email is protected during transmission.
What are the common SMTP ports, and which one is secure?
Port 25: Used between servers, not secure, often blocked.
Port 465: Secure (SMTPS), encrypted by default.
Port 587: Recommended port, works well with STARTTLS.How do I know if my email is encrypted?
Most email services (like Gmail) show a small padlock icon. A green or closed padlock usually means your email was encrypted.
What’s the difference between TLS and SSL?
SSL is the older version and is now outdated. TLS is the modern, more secure replacement and is used by most email services today.
Why is TLS needed in emails?
TLS keeps your data private and safe while it’s traveling. It protects against hackers, identity theft, and tampering.







